
Splice sequences are found at the 5′ and 3′ tails of introns marked with the dinucleotide GU at its 5′ end and AG at the 3′ end. Exons are segments containing the encoding sequence for protein synthesis, while introns are intervening segments of nucleotides that will be excised from the primary RNA transcript (pre-mRNA) in a process called splicing. The transcribed RNA contains multiple segments called exons and introns. The consensus sequence TATTAA (called TATA box) is located 25–35 bases upstream of the initiation site, followed by a poly-G/C consensus sequence located 32–38 bases upstream. The initiation complex recognizes the promoter region in the DNA as a signal for the transcription starting point. The RNA polymerases are aided in the transcription function by a series of proteins called transcription factors, which have several functions mainly to facilitate the binding of RNA polymerase II to the promoter sequence, forming the transcription initiation complex. RNA polymerase III synthesizes 5S RNA, and all transfer RNA (tRNA) is located in the nucleoplasm. Only some proteins have a quaternary structure as well. Each protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The quaternary structure also influences the three-dimensional shape of the protein and is formed through the side-chain interactions between two or more polypeptides. The three-dimensional shape of a protein, its tertiary structure, is determined by the interactions of side chains from the polypeptide backbone. These hydrogen bonds create alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheets of the secondary structure. The secondary structure contains regions of amino acid chains that are stabilized by hydrogen bonds from the polypeptide backbone. Only some proteins have a quaternary structure as well. The primary structure is comprised of a linear chain of amino acids. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure.
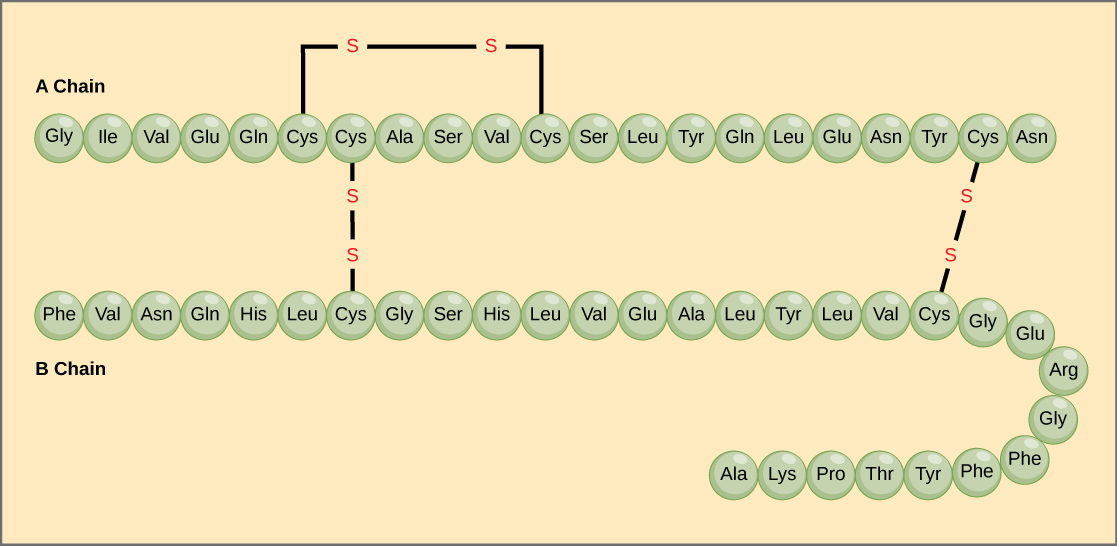
A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. They carry out a wide variety of organism functions, including DNA replication, transporting molecules, catalyzing metabolic reactions, and providing structural support to cells. Proteins are polypeptide structures consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
